Sun safety and skin health are crucial for reducing the risk of skin cancer and other harmful effects of UV radiation. Sunscreen helps to block harmful UV rays from the sun, which are known to cause skin damage and increase the risk of developing skin cancer. Regularly applying sunscreen with a high SPF (sun protection factor) is crucial for protecting the skin from harmful UV rays. It is recommended to use a broad-spectrum sunscreen of 30 or higher that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays can prematurely age the skin and contribute to skin cancer, while UVB rays are responsible for sunburns and development of non-melanoma skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
When applying sunscreen, it is important to cover all exposed areas of the body, including the face, neck, ears, arms, and legs. It should be applied generously and reapplied every two hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating. Sunscreen should also be applied 15-30 minutes before going outside to allow it to fully absorb into the skin.

In addition to sunscreen, it is essential to adopt other protective measures:
- Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses that block UV rays.
- Shade: Seek shade during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) when UV radiation is strongest.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation that significantly increases the risk of skin cancer.
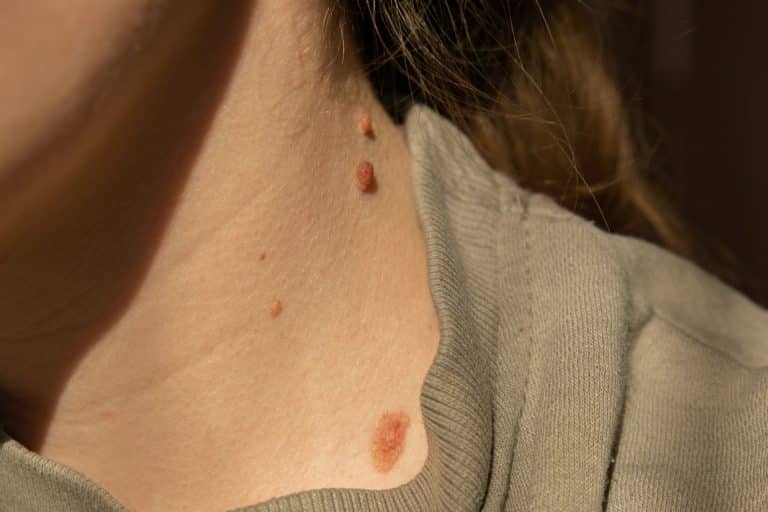
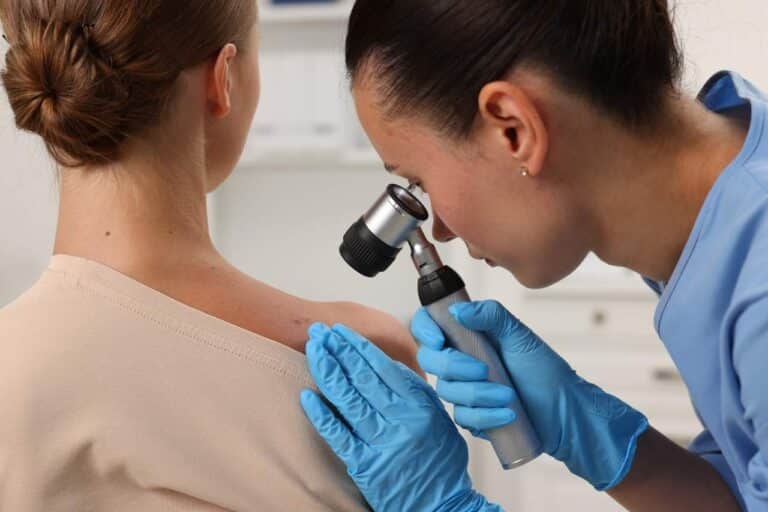
- Regular Skin Checks: Perform regular self-examinations for new or changing moles or spots on your skin and consult a dermatologist for professional screenings. This includes looking for new moles or growths, changes in existing moles such as size, shape, or colour, and any sores that do not heal.
Common Misconceptions About Sunscreen
- Higher SPF equals all day protection
A higher SPF (Sun Protection Factor) does not mean that the sunscreen will protect you all day. SPF only measures how long it takes for the skin to burn compared to unprotected skin. Regardless of SPF, sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours for optimal protection. - Sunscreen isn’t necessary on cloudy days or indoors
Clouds filter small fraction of UV rays, and UVA rays can penetrate windows, making sunscreen necessary even on cloudy days or indoors. - Immunity to sunburn while swimming
Water can amplify UV exposure by reflecting light, increasing the risk of sunburn. Sunscreen should be applied before swimming. - All sunscreen formulas are the same
Sunscreens differ in their formulations, with physical (mineral) and chemical options available. Chemical sunscreens often contain ingredients like oxybenzone, which may have harmful effects, whereas mineral sunscreens with zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are generally considered safer. - Sunscreen never expires
Sunscreens do have expiration dates, usually around three years. After this period, the active ingredients can degrade, reducing their effectiveness and leaving the skin unprotected.
Addressing these common misconceptions is crucial for ensuring proper sunscreen use and maximising its protective benefits.
Prioritising sun protection using sunscreen, protective clothing, seeking shade, and avoiding tanning beds can significantly reduce the risk of developing skin cancer. It is important to make sun protection a daily habit to maintain healthy skin and prevent the potentially life-threatening consequences of skin cancer. Remember to check your skin and book yearly skin checks with a skin doctor or dermatologist for any skin-related concerns.